Dwarf galaxies, of course, are much smaller galaxies that can be found orbiting larger ones around them. However, it is thought that the nature of dark matter may be better understood by looking at the formation of stars within galaxies.

This image shows the galaxy cluster MACS J1149.5+2223 taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope; the inset image is the very distant galaxy MACS1149-JD1, seen as it was 13.3 billion years ago and observed with ALMA. Here, the oxygen distribution detected with ALMA is depicted in red.
Over the history of the Universe, galaxies have evolved substantially. And it will take even longer timescales for large galaxies and then galaxy groups and galaxy clusters to arise. The galaxy MACS1149-JD1 is the second-most-distant galaxy ever found, whose light arrives from 530 million years after the Big Bang. These massive bursts of star formation don’t simply occur because you had a star cluster; they occur when large mergers happen, giving rise to what astronomers call a starburst. The researchers report their findings in the journal Nature.
Some called starburst galaxies are forming stars at a tremendous rate, and the young stars heat the hydrogen to make it glow. These are called active galactic nuclei ( AGNs ) and are often seen glowing at X-ray wavelengths. For decades, scientists have been trying to directly detect the rare instances where dark matter interacts with the regular stuff.
 This artist’s impression shows the Milky Way galaxy. Two stars shine through the center of a ring of cascading dust in this image taken by the NASA ESA Hubble Space Telescope. It’s the glue that holds visible matter in galaxies – stars and gas – together. based on the colors of its globular clusters, the galaxy is about 10 billion years old. It resides about 65 million light-years away.
This artist’s impression shows the Milky Way galaxy. Two stars shine through the center of a ring of cascading dust in this image taken by the NASA ESA Hubble Space Telescope. It’s the glue that holds visible matter in galaxies – stars and gas – together. based on the colors of its globular clusters, the galaxy is about 10 billion years old. It resides about 65 million light-years away.
Finding a galaxy without any is completely unexpected; it challenges standard ideas of how galaxies work. Given the object’s large size and faint appearance, astronomers classify NGC 1052-DF2 as an ultra – diffuse galaxy. From those measurements, the team calculated the galaxy’s mass.
The stars in the galaxy can account for all the mass, and there doesn’t seem to be any room for dark matter, Pieter van Dokkum of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut, lead researcher of the Hubble observations said.
But it doesn’t look like an elliptical galaxy, either. Or did the growth of the nearby massive elliptical galaxy NGC 1052 billions of years ago play a role in NGC 1052-DF2‘s dark matter deficiency? Three new dark matter experiments are moving ahead with funding from the U. S. Department of Energy and the U. S. National Science Foundation – will one of them finally capture a glimpse of the universe’s most elusive material?
The galaxy without dark matter stunned scientists. The Universe, despite all the planets, stars, gas, dust, galaxies, and more we find within it, doesn’t quite add up. One consequence of dark matter’s existence is that it implies that every large structure that forms in the Universe, such as a galaxy, will have a large, diffuse halo of dark matter surrounding it. But where we are, just 25,000 light years from the galactic center, normal matter is locally more abundant than dark matter. Over the course of your life, about a milligram of dark matter has passed through you. The universe is vast and awesome, and for the first time we are…
That means some slow rotating neutron stars are just neutron stars. Why doesn’t dark matter clump?
We are busily searching for suitable pulsars near large amounts of expected dark matter, said Michael Kramer, director at MPIfR.
An international team of astronomers has identified huge star streams in the outskirts of two nearby spiral galaxies. The planets, stars, galaxies, and everything else that we see makes up just 4.9 percent of the stuff in the universe. So-called ordinary matter – including stars, gases, dust, planets and everything on them – accounts for only five percent of all content in the Universe. The leading contender for a dark matter particle is a class of weakly interacting massive particle ( WIMP ), which is similar to another subatomic particle called a neutrino in that it rarely interacts with other matter.
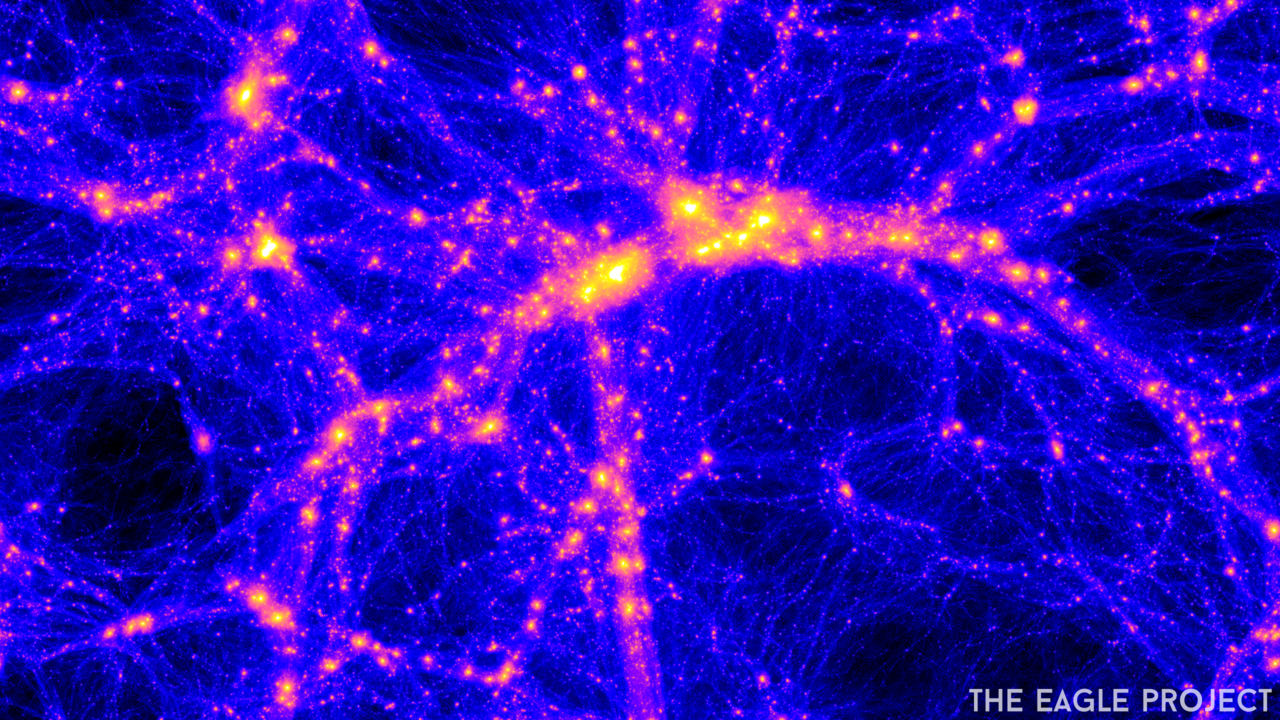
Image Credits: The EAGLE Project. A simulation of galaxies forming in the early Universe. By chance, some of them experience a history that’s similar to the Milky Way’s.